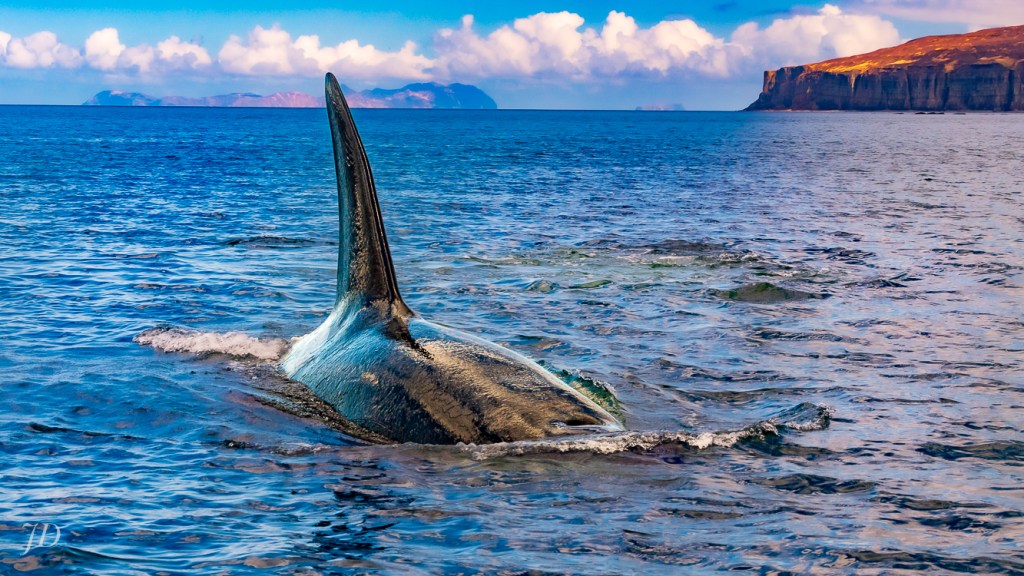
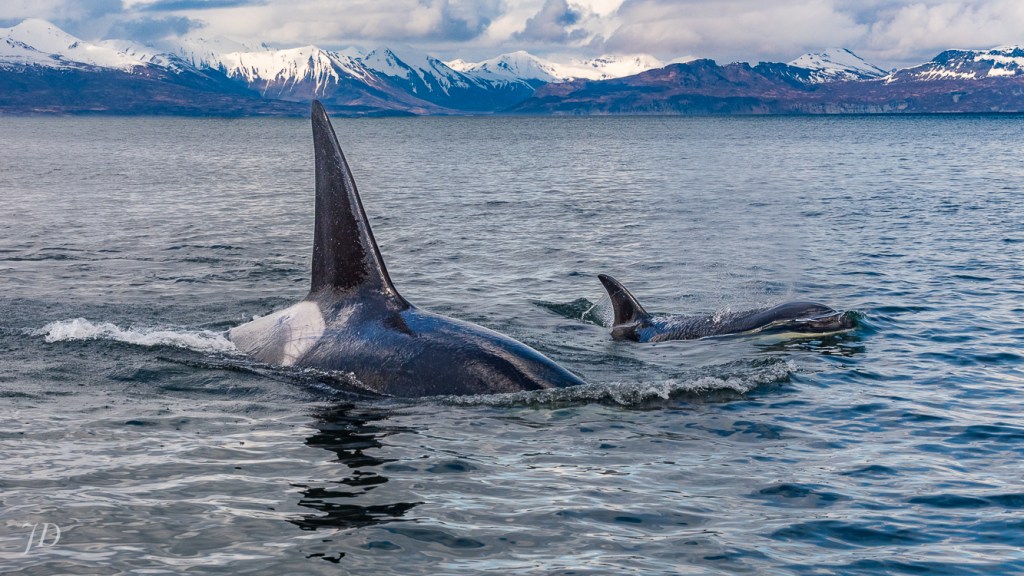
Twice the male Orca swam beneath our small skiff, so near the hull we could see him plainly through the Alaska Gulf’s semi-clear water. Each time, he emerged on the other side very close, turning parallel with our watercraft, eyeing us. Using our 20-foot skiff as a comparison, I estimate his length at over 25 feet in length, shimmering, bulky, muscular, liquid, graceful. Was he simply curious? Cautiously keeping us in check while his mate and daughters practiced hunting with the still living seal she’d carried out into open sea to the left of this photo? Showing off? Warning us? Each time the male came in close our hearts rose in our chests, our breath stuck in our throats. I blew those shots, able to fit only a fraction of his massive body in the frame created by the 70mm lens, shutter speed too slow to freeze him as his movements always appeared slower than they actually were. But I did get this capture of him swimming in for one of those dives beneath our boat.
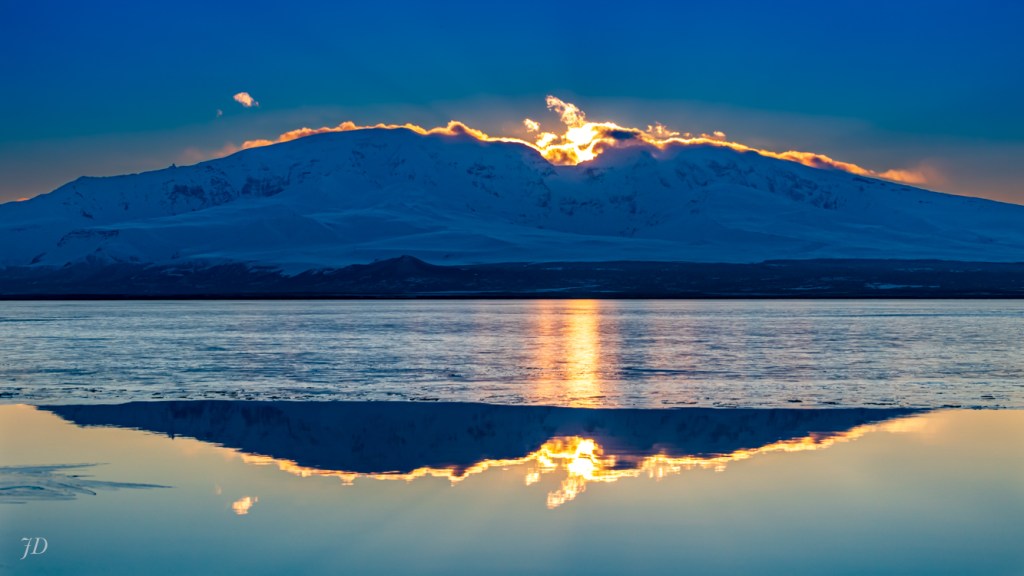
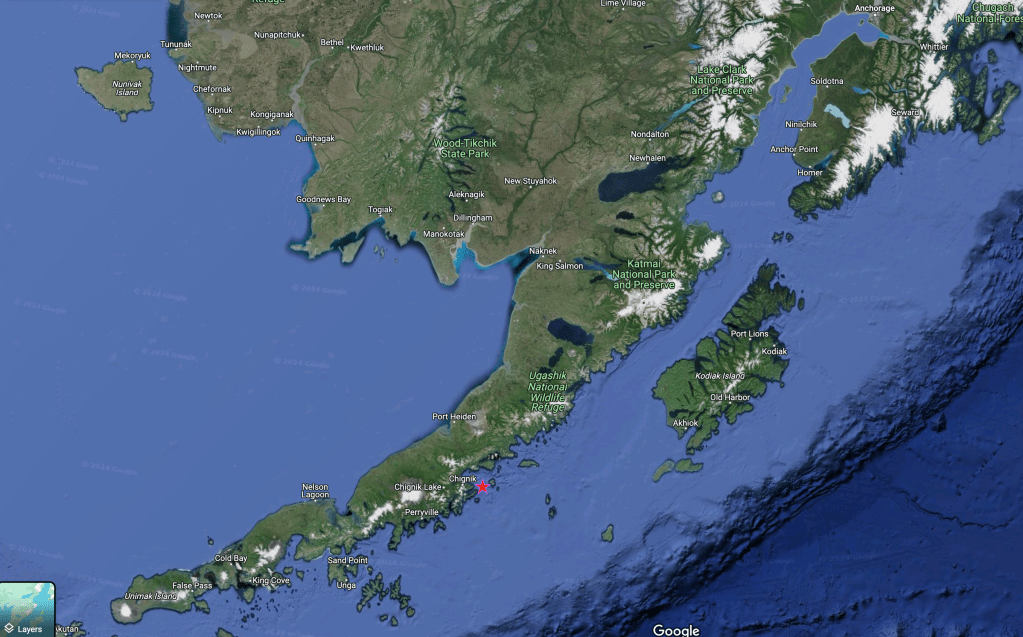
The light was in and out throughout the encounter, the sun at times obscured behind dark clouds, at other times breaking through clear blue skies. Here dappled light is filtered through thin clouds, creating a rainbow-like effect accentuating blues, mauves and purples. This image is interesting for the background landscape as well. The land mass to the left is Nakchamik Island. The smaller island to the right is the smaller of the two Kak Islands. On the right is (I think) Little Castle Cape on the mainland.
JD, Chignik Bay, Gulf of Alaska, May 6, 2018